Rotary Tables 101: Top Vertex & Tilting Options to Know
Rotary Tables 101: Top Vertex & Tilting Options to Know
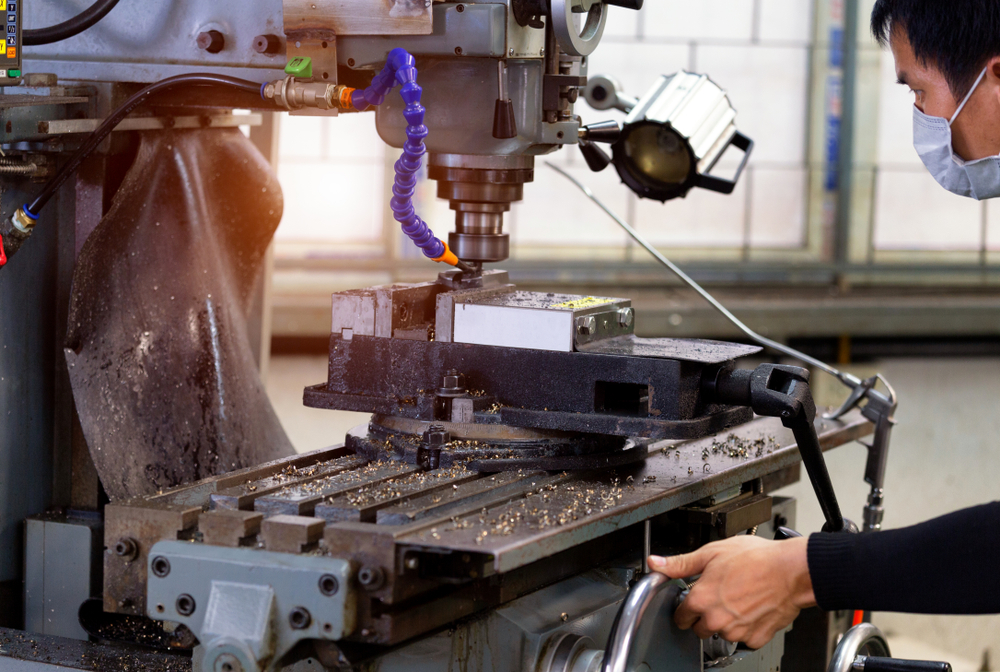
In the high-stakes world of precision manufacturing, time is measured in micron tolerances and cycle times. While multi-million dollar machining centers capture the limelight, the true workhorses of the shop floor are often the accessories that enable multi-axis capability and indexing accuracy. No accessory is more critical to unlocking the full potential of your vertical or horizontal machining center than the rotary table.
The right rotary table can transform a standard 3-axis machine into a highly efficient 4-axis power player, slashing setup times and enabling complex geometries previously relegated to expensive, dedicated machinery.
This blog will delve deep into the essential rotary table uses, key distinctions like the horizontal vs vertical rotary table setup, and the specialized features you need to consider for maximizing throughput.
The Unsung Hero: What is a Rotary Table?
At its core, a rotary table is a precision work positioning device that holds a workpiece and rotates it accurately about a central axis. Mounted directly onto the bed of a milling machine, a rotary table enables the operator or CNC program to perform circular indexing, angular spacing, and complex contouring.
Core Rotary Table Uses
- Indexing and Spacing: Creating bolt circles, gear teeth, splines, or hex flats at precise, repeatable angular intervals.
- Circular Milling: Machining large radius arcs or full circular profiles, such as those found in cams or large flanges.
- Angular Machining: On a tilting rotary table, machining compound angles or drilling features on inclined surfaces without complex fixtures.
Classifying Rotary Tables: Manual, Tilting, and CNC
When selecting the best rotary table for milling, you must distinguish between the main operational types, each suited for different shop floor realities.
1. Manual Indexing and the Dividing Head
The traditional rotary table uses a worm gear ratio (often 40:1, 60:1, or 90:1) for fine control. A crucial component here is the rotary table dividing head (or indexing plate set), which uses a series of drilled plates to facilitate precise angular division—think 24, 48, 60, or 120 divisions.
- Pros: Cost-effective, simple to operate, suitable for shops focused on manual or simpler indexing tasks.
- Cons: Time-consuming setup, reliance on operator calculation, lower overall accuracy compared to electronic models.
2. Horizontal vs. Vertical Rotary Table
This distinction refers to the orientation of the table's rotational axis relative to the machine bed, offering flexibility in how the workpiece is presented to the cutting tool.
- Horizontal: The axis is parallel to the floor, often used for circular milling or when maximum rigidity is needed on a VMC (Vertical Machining Center). The workpiece lies flat on the table face.
- Vertical: The axis is perpendicular to the floor, ideal for indexing long, slender parts (like shafts or long gears) or when the workpiece geometry requires it to stand tall. Many modern tables are designed as "HV" models, meaning they can be easily mounted and used in either horizontal vs vertical rotary table orientation.
3. The Tilting Rotary Table: Complexity in One Setup
For work requiring compound angles, parts that need rotation and an incline, the tilting rotary table is indispensable. This type features a secondary axis of motion, allowing the table surface to be tilted, typically from 0 to 90 degrees.
- Benefit: Enables machining on multiple faces of a part in a single setup, drastically reducing cumulative errors and streamlining workflow. These tables are essential for tapered surfaces, angular drilling, or intricate mold work.
4. CNC Rotary Table: The Future of Precision
The modern machine shop relies on the CNC rotary table (often called a 4th or 5th axis). These utilize direct drive or high-precision gear systems integrated seamlessly into the machine's CNC controller.
- Market Trend: The rise of simultaneous 5-axis machining is heavily driven by these tables. The top segment in the market is currently 5-axis Rotary Tables, accounting for a 46% share of the total CNC rotary table market, illustrating the industry's shift toward highly complex part production.
- Advantages: Unmatched speed, resolution, and dynamic accuracy. Direct drive systems, in particular, eliminate backlash, making them perfect for contour milling where the rotary axis is moving simultaneously with the linear axes. Furthermore, the global High-Precision Direct Drive Rotary Tables market is expanding at a CAGR of 6.8% (2024-2031), showing a clear investment focus on speed and accuracy.
Focus on Quality: The Vertex Rotary Table Standard
When examining workholding options, brands known for durability and precision stand out. The Vertex rotary table, for instance, is a common benchmark in industrial settings. Vertex tables are often praised for their robust Meehanite castings, hardened and ground worm gears, and the inclusion of disengageable worm mechanisms for quick manual rotation and setup, a feature critical for balancing CNC integration with hands-on adjustment.
We offer a curated selection of rotary tables from industry-leading manufacturers, including Vertex, Phase II, Precise, YUASA, and Palmgren, promising not just precision (often guaranteed by an inspection certificate) but also longevity on the demanding factory floor.
Key Selection Criteria: Finding the Right Match
Choosing the right rotary table for milling machine applications requires meticulous consideration:
- Size and Capacity: The table diameter must match the machine's capacity and the typical size of your workpieces. Crucially, the table’s height (or "low profile") affects the machine's Z-axis travel.
- Indexing Accuracy (Arc Seconds): This is the paramount specification. High-precision CNC rotary table units should offer accuracy measured in a few arc seconds, while quality manual tables typically range from 30 to 60 arc seconds.
- Worm Gear Ratio: A higher ratio (e.g., 90:1) offers finer positioning capability, ideal for critical, high-tolerance work.
- Rigidity and Clamping: For heavy-duty milling machine rotary table applications, look for robust clamping mechanisms that securely lock the table, preventing movement or vibration during aggressive cutting. This is particularly vital since milling equipment holds the largest share (29.43%) of the US machine tools market, emphasizing the need for robust accessories.
The decision to invest in a high-quality rotary table for milling machine operations isn't just a technical one; it’s a strategic business decision. By minimizing setup time and maximizing part complexity in a single fixturing, rotary tables directly increase machine utilization and reduce per-part cost. Penn Tool Co. specializes in providing a complete range of precision rotary tables and related workholding accessories designed to seamlessly integrate into your existing VMCs and HMCs, ensuring you find the right balance of price point and high-performance capability.